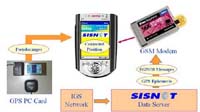
 |
 |
|
SISNeT handheld
receiver (based on an iPAQ PDA)
|
|
Signals used by SISNeT
SISNeT (Signal in Space through the Internet) uses signals
from EGNOS, the European Geostationary Navigation Overlay
Service.
EGNOS is the first step in the European contribution to the
Global Navigation Satellite System, and a fundamental stepping-stone
towards Galileo, Europe's own Global Navigation Satellite
System. EGNOS is an augmentation system to the GPS (Global
Positioning Satellite) satellite navigation system,
which provides and guarantees navigation signals for aeronautical,
maritime and land mobile Trans-European network applications.
Satellite broadcasting through geostationary satellites (GEOs)
has proved to be an efficient strategy for avionic applications
and other modes of transport. For some applications though,
GEO broadcasting may have some limitations due to obstacles like buildings
in cities or rural canyons can interfere with the
GEO reception.
While the EGNOS messages will still be very useful for transport
applications, a different transmission link may be needed
to take full advantage of the EGNOS potential. For this reason,
ESA had launched specific contract activities (through
the Advanced System Telecommunication Equipment programme
-ASTE-) to assess and demonstrate architectures where the
EGNOS signal was broadcast through non-GEO means (e.g. FM or
GSM broadcasting). In this context, ESA launched an internal
project to provide access to the these messages through
the Internet. This project is called SISNeT.
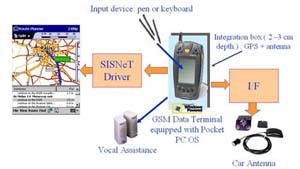
SISNeT receiver based on a GSM / GPRS
terminal
SISNeT availability
In August 2001, the ESA GNSS-1 Project Office set up the first
prototype of the SISNeT concept. This prototype uses a PC
computer to implement the user equipment software. The connection
to the Internet was achieved using a LAN environment (via
a proxy server).
Since February 2002, the SISNeT service has been available
to the users via open Internet through an authentication protocol (see
the SISNeT User Interface Document - for more details).
Developments
In the past, some of the ESA contracts were aimed at developing
EGNOS SISNeT-powered receivers and demonstrating what they
could do. These contracts included:
- Development of an integrated SISNeT receiver, containing
a GPS receiver and a GSM / GPRS modem (in co-operation with
GMV under ESA contract);
- Demonstrations of SISNeT receivers embedded in cars and
buses (in co-operation with GMV under ESA contract);
- Integration of the SISNeT technology in professional
software tools (in co-operation with GMV under ESA contract);
- Development of a handheld SISNeT receiver, based on an
iPAQ PDA (Personal Digital Assistant) (in co-operation with
the Finish Geodetic Institute under ESA contract);
- Development of a SISNeT receiver based on a GSM (Global
System for Mobile communications) terminal (in co-operation
with the Navocap society under ESA contract);
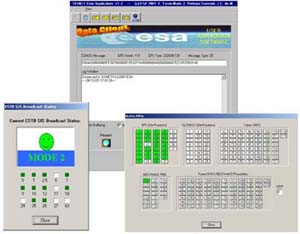
Monitoring the active satellites
and the EGNOS broadcast status using the SISNeT User Application
Software
Opportunities for SISNeT
The SISNET project can deliver significant benefits to the
GPS land-user community. A user equipped with a GPS (Global
Positioning Satellite) receiver and a GSM (or GPRS) modem
can access the SISNET services and benefit from the EGNOS
augmentation signals, even under situations of GEO blocking.
The combination of the power of EGNOS and the almost unlimited
capabilities of the Internet offers the opportunity for the
development of a multitude of applications for satellite navigation.
To stay in touch with the progress of SISNeT technology, please
do not forget to periodically visit the ESA SISNeT website.
|

